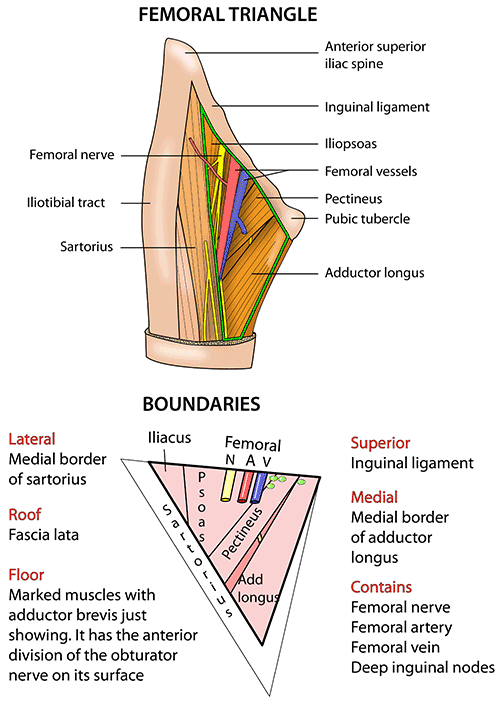
FEMORAL TRIANGLE
FEMORAL TRIANGLE
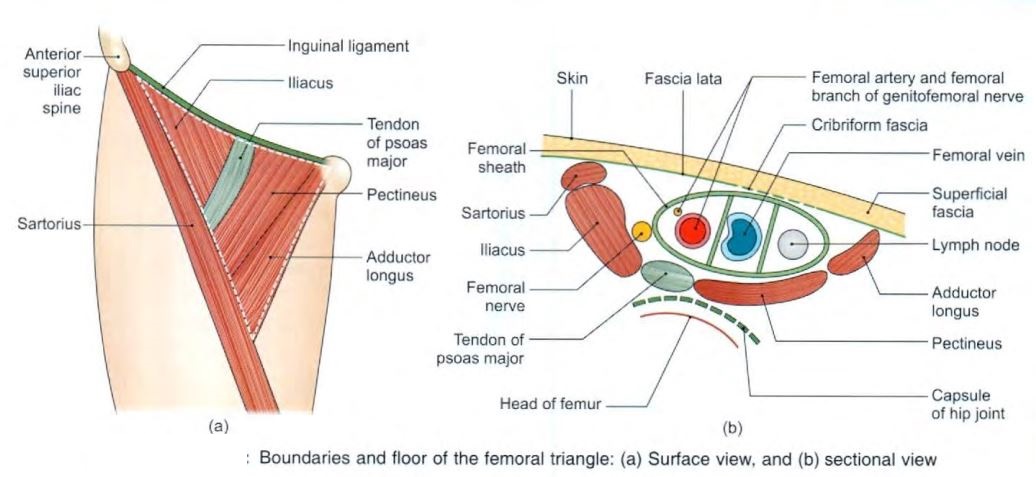
- boundaries
- apex
- formed by a point where medial and lateral boundaries meet
- roof
- floor
- laterally
- medial border of sartorius
- medially
- medial border of adductor longus
- base
- inguinal ligament
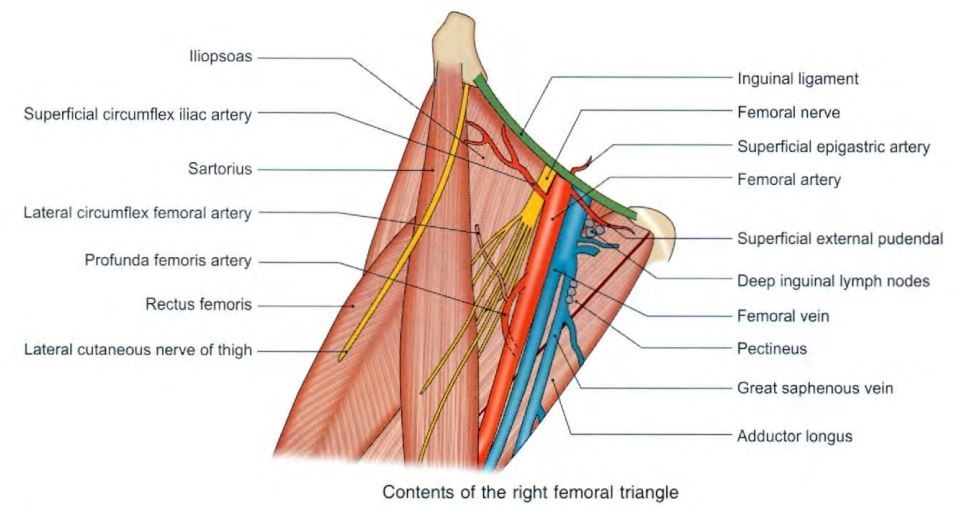
- contents
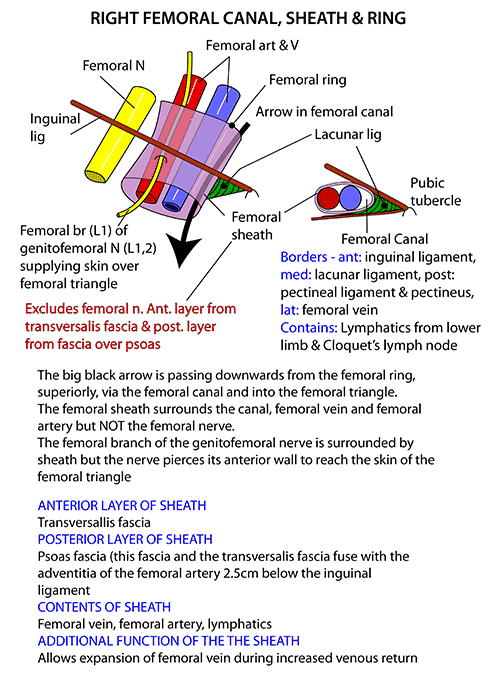
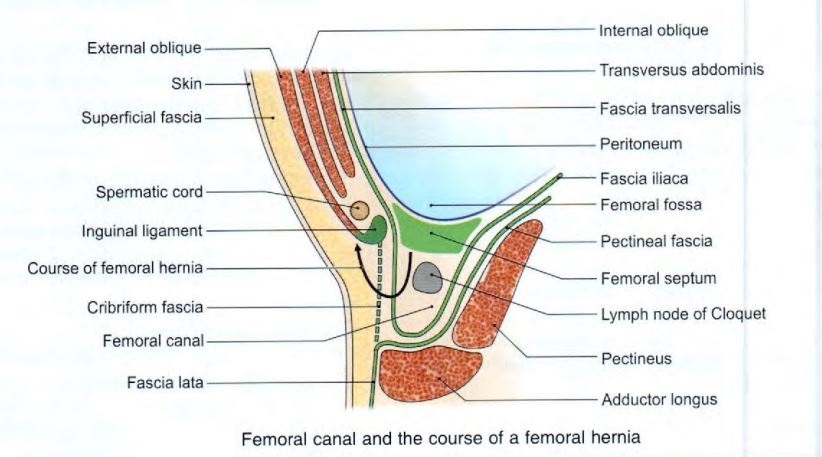
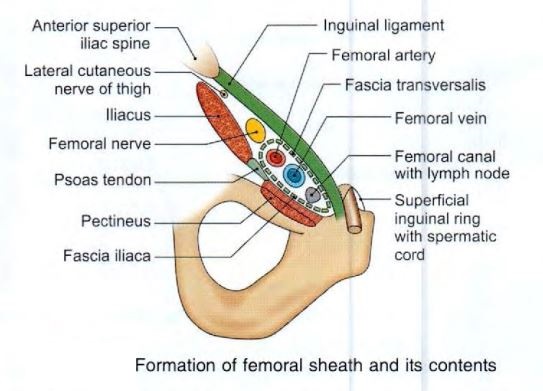
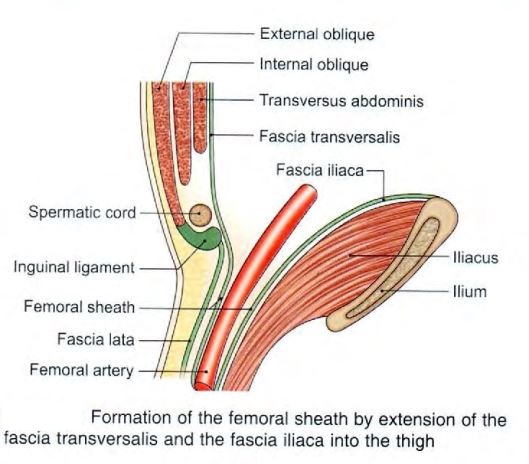
- femoral sheath
- The femoral sheath encloses the upper 4 cm of the femoral vessels
- funnel shaped sleeve of fascia
- formed by downward extension of 2 layers of abdomen fascia
- anterior wall by fascia transversalis
- posterior wall by fascia iliaca
- lateral wall is vertical
- medial wall is oblique
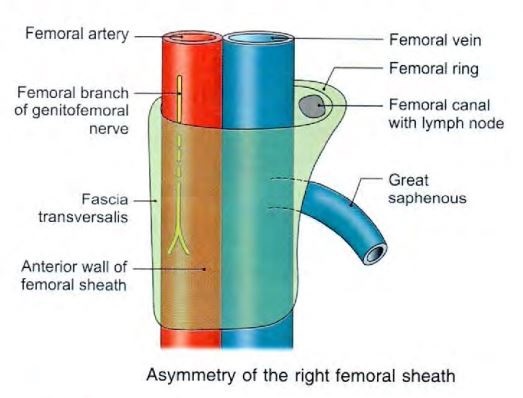
- divided in to 3 compartments
- lateral or arterial compartment
- medial or lymphatic compartment
- intermediate or venous compartment
- femoral vein
- The femoral vein accompanies the femoral artery. The vein is medial to the artery at base of triangle, but posteromedial to artery at the apex
- The femoral vein receives the grea t saphenous vein, circumflex veins and veins corresponding to the branches of femoral artery
- femoral canal
- medial compartment of femoral sheath
- contains a lymph node called cloquet of rosenmuller
- The base or upper end of femoral canal is called femoral ring
- conical in shape
- boundaries
- anteriorly by inguinal ligament
- posteriorly by pectineus
- medially by lacunar ligament
- laterally by septum separating from femoral vein
- femoral fossa
- The parietal peritoneum covering sep tum from above shows a depression called femoral fossa
- femoral septum
- The femoral ring is closed by a condensation of
- extraperitoneal connective tissue called the femoral septum
- deep inguinal lymph nodes




Discussion