हड्डी के संरचनात्मक नाम
Many anatomical terms descriptive of bone are defined in anatomical terminology, and are often derived from Greek and Latin.
हड्डी के प्रकार
लंबे हड्डी
- Main article: Long bone
A long bone is one that is cylindrical in shape, being longer than it is wide. However, the term describes the shape of a bone, not its size, which is relative. Long bones are found in the arms (humerus, ulna, radius) and legs (femur, tibia, fibula), as well as in the fingers (metacarpals, phalanges) and toes (metatarsals, phalanges). Long bones function as levers; they move when muscles contract. They are responsible for the body's height.
छोटे हड्डी
- Main article: Short bone
A short bone is one that is cube-like in shape, being approximately equal in length, width, and thickness. The only short bones in the human skeleton are in the carpals of the wrists and the tarsals of the ankles. Short bones provide stability and support as well as some limited motion.
चिपटे हड्डी
- Main article: Flat bone
The term “flat bone” is something of a misnomer because, although a flat bone is typically thin, it is also often curved. Examples include the cranial (skull) bones, the scapulae (shoulder blades), the sternum (breastbone), and the ribs. Flat bones serve as points of attachment for muscles and often protect internal organs. Flat bones do not have a medullary cavity because they are thin.
निराकार हड्डी
- Main article: Irregular bone
An irregular bone is one that does not have an easily classified shape and defies description. These bones tend to have more complex shapes, like the vertebrae that support the spinal cord and protect it from compressive forces. Many facial bones, particularly the ones containing sinuses, are classified as irregular bones.
Sesamoid bones
A sesamoid bone is a small, round bone that, as the name suggests, is shaped like a sesame seed. These bones form in tendons (the sheaths of tissue that connect bones to muscles) where a great deal of pressure is generated in a joint. The sesamoid bones protect tendons by helping them overcome compressive forces. Sesamoid bones vary in number and placement from person to person but are typically found in tendons associated with the feet, hands, and knees. The only type of sesamoid bone that is common to everybody is the kneecap (patella, pl. patellae) which is also the largest of the sesamoid bones.
बहिर्गत
गोलाकार
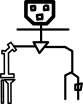
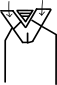
Different types of bone markings and features. A condyle(उभार,स्थूलक) is the round prominence at the end of a bone, most often part of a joint – an articulation with another bone. The epicondyle refers to a projection near a condyle, particularly the medial epicondyle of the humerus. These terms derive from Greek.
An eminence (उत्सेध) refers to a relatively small projection or bump, particularly of bone, such as the medial eminence.
A process(प्रवर्ध) refers to a relatively large projection or prominent bump, as does a promontory such as the sacral promontory.eg., petrosal p. — अश्म प्रवर्ध , pterygoid p. — पक्षाभ प्रवर्ध , sphenoidal p. — जतूक प्रवर्ध , spinous p. — कशेरुका कंटक प्रवर्ध , styloid p. — शर प्रवर्ध , supra-condyloid p. — अधिस्थूलकाभ प्रवर्ध , xiphoid p. — उरोस्थि प्रवर्ध , zygomatic p. — गंड प्रवर्ध , संधि प्रवर्ध (articular p) , infundibular p (कीपाकार प्रवर्ध ) , mastoid p (कर्णमूल प्रवर्ध) , coracoid p , Zygomatic p , anterior clinoid p , palatine p, transverse p. — (कशेरुका) अनुप्रस्थ प्रवर्ध, olecranon p (कूर्पर प्रवर्ध) , odontoid p. (dens) — दंताभ प्रवर्ध , notched xiphoid p. — सभंगिका उरोस्थि प्रवर्ध , lacrimal p. — अश्रु प्रवर्ध , infraorbital p. — अवनेत्रगुहा प्रवर्ध ,
Both tubercle(गुलिका) and tuberosity (गंडक ) refer to a projection or bump with a roughened surface, with a tubercle generally smaller than a tuberosity. These terms are derived from Tuber (Latin: swelling).eg., adductor t. — अभिवर्तनी गुलिका , articular t. — संधि गुलिका , mental t. — चिबुक गुलिका , supraglenoid t. — अध्यसंगर्त गुलिका
tuberosity — गंडक
- deltoid t. — त्रिकोणिका गंडक
- frontal t. (=frontal eminence) — ललाट गंडक (ललाट उत्सेध)
- greater t. — बृहत् गंडक
- lesser t. — लघु गंडक
- navicular t. — नौकाभ गंडक
- parietal t. (=pariental eminence) — पार्श्विका गंडक (पार्श्विका उत्सेध)
- tibial t. — अंतर्जंघिका गंडक
A ramus (प्रशाखा ) (Latin: branch) refers to an extension of bone, such as the ramus of the mandible in the jaw or Superior pubic ramus. Ramus may also be used to refer to nerves, such as the ramus communicans.
A facet (पृष्ठ , फलक) refers to a small, flattened articular surface.
| feature | Examples | |
|---|---|---|
| अधिस्थूलक | epicondyle | मध्यस्थ अधिस्थूलक (medial epicondyle) , पार्श्व अधिस्थूलक (lateral epicondyle) |
| उत्सेध | eminence | medial eminence , parietal e.(पार्श्विका उत्सेध) , |
| उभाड़ , गूमड़ | protuberance | mental protuberance , external occipital protuberance , |
| उभार , स्थूलक | condyle | occipital condyle,medial condyle , lateral condyle |
| गंडक | tuberosity | delotid tuberosity , ischial tuberosity , radial tuberosity , ulnar tuberosity , |
| गुलिका | tubercle | greater tubercle , lesser tubercle,pubic tubercle , iliac tubercle , adductor tubercle , conoid tubercle, infra glenoid tubercle, |
| प्रवर्ध | process | अंसकूट प्रवर्ध (acromion process) |
| भूनसिका , प्रोत्तुंग | promontory | sacral promontory |
| प्रशाखा | ramus | greater ramus , ramus of mandible , pubic ramus |
Pointed
A line (रेखा ) refers to a long, thin projection, often with a rough surface.
Ridge (कटक) and crest (शिखा) refer to a long, narrow line. Unlike many words used to describe anatomical terms, the word ridge is derived from Old English. eg.,
- crest — शिखा
- frontal c. — ललाटशिखा
- iliac c. — श्रोणि फलक शिखा
- infra temporal c. — अवशंख शिखा
- internal occipital c. — आभ्यंतर पश्चकपाल शिखा
- interosseous c. — अंतरा अस्थि शिखा
- lacrimal c. — अश्रु शिखा
- median longitudinal c. — मध्य अनुदैर्घ्य शिखा
- neural c. — तंत्रिका शिखा
- posterior lacrimal c. — पश्चाश्रु शिखा
- sacral c. — त्रिक शिखा
- sacral articular c. — त्रिक संधायक शिखा
- sphenoid c. — जतुक शिखा
- tibial c. — अंतर्जंघिका शिखा
- ridge — कटक
- supracondylar r. — अधिस्थूलक कटक
- supraorbital r. — अधिनेत्रगुहा कटक
A spine(कंटिका ) , as well as referring to the spinal cord, may be used to describe a relatively long, thin projection or bump.
| feature | example | |
|---|---|---|
| कंटिका | spine | spinous process , spine of scapula , iliac spine , ischial spine |
| कटक | ridge | supracondylar ridge |
| रेखा | line | linea aspera , mylohyoid line , trapezoid line |
| शिखा | crest | iliac crest , pubic crest |
| पृष्ठ , फलक | facet | demifacet , facet joint , acromial facet , sternal facet , articular facet |
Special
These terms are used to describe bony protuberances in specific parts of the body.
The Malleolus (Latin: small hammer) is the bony prominence on each side of the ankle. These are known as the medial and lateral malleolus. Each leg is supported by two bones, the tibia on the inner side (medial) of the leg and the fibula on the outer side (lateral) of the leg. The medial malleolus is the prominence on the inner side of the ankle, formed by the lower end of the tibia. The lateral malleolus is the prominence on the outer side of the ankle, formed by the lower end of the fibula.
The trochanters are parts of the femur, to which muscles attach. It may refer to the greater, lesser, or third trochanter
| feature | example | |
|---|---|---|
| गुल्फ | malleolus | medial malleolus , lateral malleolus |
| चक्रिका | disc | lateral disc |
| चाप | arch | medial arch |
| शिखरक | trochanter | greater trochanter , lesser trochanter |
| सौंफ | fennel | fennel |
| pedicle |
Cavities
Openings The following terms are used to describe cavities that connect to other areas:
A foramen (रन्द्र,छिद्र ) is any opening, particularly referring to those in bone. Foramina inside the body of humans and other animals typically allow muscles, nerves, arteries, veins, or other structures to connect one part of the body with another.
- foramen — रंध्र
- anterior ethmoid f. — अग्रझर्झरिका रंध्र
- carotico-clinoid f. — केरोटिको स्थाणुक रंध्र, केरोटिको-क्लिनॉइड रंध्र
- carotid f. — कैरोटिड रंध्र
- entocarotid f. — अंतः कैरोटिड रंध्र
- epiploic f. (aditus to the lesser sac, foramen Winslow) — वपा रंध्र
- greater sciatic f. — बृहत् आसन रंध्र
- hypoglossal f. — अधोजिह्व रंध्र
- incisive f. — कृंतक रंध्र
- infra orbital f. — अवनेत्र रंध्र
- interatrial f. — अंतरा अलिंद रंध्र
- interventricular f. — अंतरा निलय रंध्र
- jugular f. — गंडिका रंध्र
- lesser sciatic f. — लघु आसन रंध्र
- mastoid f. (foramen mastoidae) — कर्णमूल रंध्र
- mental f. — चिबुक रंध्र
- nutrient f. — पोषक रंध्र
- optic f. — नेत्रगुहा रंध्र
- parietal f. — पार्श्विका रंध्र
- postglenoid f. — अंसगर्तपश्च रंध्र
- primary interatrial f. (ostium primum) — प्राथमिक अंतरा अलिंद रंध्र
- sacral f. — त्रिक रंध्र
- stylomastoid f. — शर कर्णमूल रंध्र
- zygomaticofacial f. (foramen zygomatico facialis) — गंडानन रंध्र, जाइगोमैटिको फेशियल रंध्र
- zygomatico orbital f. — गंड-नेत्रगुहा रंध्र, ज़ाइगोमैटिको ऑर्बिटल रंध्र
- f. bursae omentimajoris — बृहद्वपासीरसी पुटी रंध्र
- f. caecum — अंध रंध्र
- f. laceratum (f. lacerum) (foramen lauratio) — विषम रंध्र
- f. magnum — महा रंध्र
- f. of Magendie — मैजेंडी रंध्र
- f. ovale — अंडाकार रंध्र
- f. rotundum — वर्तुल रंध्र
- f. singulare — एकल रंध्र
- f. spinosum — कंटक रंध्र
- f. transversarium — अनुप्रस्थ प्रवर्ध रंध्र
- f. Vesalii — वैसाली रंध्र
A canal(नली , is a long, tunnel-like foramen, usually a passage for notable nerves or blood vessels.
Blind-ended The following terms are used to describe cavities that do not connect to other areas:
A fossa ( गर्त ) (from the Latin fossa, ditch or trench) is a depression or hollow, usually in a bone, such as the hypophyseal fossa, the depression in the sphenoid bone.
- fossa — खात
- canine f. — रदनक खात
- condyloid f. — स्थूलकाभ खात
- coronoid f. — चंचु खात
- cranial f. — कपाल खात
- femoral f. — और्वी खात,फेमोरल खात
- glenoid f. — गिलनॉइड खात
- hyaloid f. — काचाभ खात
- incisive f. — कृंतक खात
- jugular f. — ग्रीवा खात
- lacrimal f. — अश्रु खात
- mandibular f. — अधोहनु खात
- olecranon f. — कूर्पर खात
- orbital f. — नेत्रगुहा खात
- pterygoid f. — पक्षाभ खात
- scaphoid f. — नौकाभ खात
- subarcuate f. — उपचापाकार खात
- suborbital f. — अधोनेत्रगुहा खात
- verminian f. — कटिक खात
- vestibular f. — प्रघाण खात
- zygomatic f. — गंड खात
- f. incudis — स्थूणक खात
- f. navicularis — नौकाभ खात
- f. navicularis — मूलमार्ग का नौकाभ खात
A meatus is a short canal that opens to another part of the body.
A fovea (Latin: pit) is a small pit, usually on the head of a bone. An example of a fovea is the fovea capitis of the head of the femur.
| Feature | example | |
|---|---|---|
| कुहर , नलिकापथ | meatus | acoustic meatus (internal and external , |
| खांच | notch | radial notch , sternal notch , suprascapular notch , ulnar notch , trochlear notch , fibular noitch |
| खातिका | groove | radial groove , intertubercular groove , bicipital groove , mylohyoid groove , costal groove , subclavian groove |
| गर्त | fossa | cranial fossa , pterygopalatine fossa ,mandibular fossa , supraspinous fossa , infraspinous fossa , coronoid fossa , cranial fossa , radial fossa , olecranon fossa |
| गर्तिका | fovea | fovea capitis |
| गावाक्ष | fenestra | fenestra |
| झोली | sella | tuberculum sellar,sella turcica |
| द्वार | opening | opening |
| नली | canal | incisive canal, Hypoglossal canal , optic canal |
| परिखा | sulcus | intertubercular sulcus |
| रंध्र , छिद्र | foramen | Foramen spinosum , foramen rotundum , foramen ovale , foramen lacerum , foramen Magnum , internal jugular foramen , incisive foramen , palatine foramen ,vertebral foramen |
| विदर | fissure | superior orbital fissure |
- orbital f. — नेत्रगुहा विदर
- petrotympanic f. — अश्म मध्य कर्ण विदर
- pterygoid f. — पक्षाभ विदर, टेरीगॉयड विदर
- pterygomaxillary f. — पक्षाभ ऊर्ध्वहनु विदर, टैरीगोमेक्सलरी विदर
- rhinal f. — घ्राण विदर, नासा विदर
- sphenoidal f. — जतूक विदर स्फिनॉइडल विदर
- squamotympanic f. — पट्टक-मध्यकर्ण-विदर, स्क्वेमो टिम्पेनिक विदर
- superior orbital f. — अधिनेत्रगुहा विदर
- supra orbital f. — अधिनेत्रगुहा विदर
- groove — खातिका
- alveolabial g. — उलूखल-ओष्ठ खातिका
- alveolingual g. — उलूखल-जिह्वा खातिका
- bicipital g. — द्विशिरस्का खातिका
- frontal g. — ललाट खातिका
- genital g. — जननेंद्रिय खातिका
- infraorbital g. — अवनेत्र-गुहा खातिका
- lacrimal g. — अश्रु खातिका
- nasolabial g. — नासा-ओष्ठ खातिका
- nasopalatine g. — नासा-तालु खातिका
- neural g. — तंत्रिका खातिका
- occipital g. — पश्चकपाल खातिका
- sacral g. — त्रिक खातिका
- urethral g. — मूत्रमार्ग खातिका
Walls
The following terms are used to describe the walls of a cavity:
A labyrinth refers to the bony labyrinth and membranous labyrinth, components of the inner ear, due to their fine and complex structure.
A sinus refers to a bony cavity, usually within the skull.
| पत्तल , थाली | perpendicular plate , cribriform plate , ptergoid plates |
| पट्ट | nasal septum |
| विवर | frontal sinus , maxillary sinus , spheroid sinus |
| भंवरजाल , भूलभुलैया | membranous labyrinth |
Joints
Main article: Joint A joint, or articulation is the region where adjacent bones contact each other, for example the elbow, shoulder, or costovertebral joint. Terms that refer to joints include:
articular process, referring to a projection that contacts an adjacent bone. suture, referring to an articulation between cranial bones. Features of long bones
Gross overview of the features of long bones in a fully grown adult. Gross features Bones are commonly described with the terms head, neck, shaft, body and base
The head of a bone usually refers to the proximal end of the bone. The shaft refers to the elongated sections of long bone, and the neck the segment between the head and shaft (or body). The end of the long bone opposite to the head is known as the base.
Internal regions
The epiphyseal plate is the area in which bone growth occurs after birth through endochondral ossification. More information Bone feature, Definition … Internal and external
Inside of the head of femur, showing surface of the bone, red and yellow bone marrow. The cortex of a bone is used to refer to its outer layers, and medulla used to refer to the inner surface of the bone. Red marrow, in which blood is formed is present in spongy bone as well as in the medullary cavity, while the fatty yellow marrow is present primarily in the medullary cavity.
- promontory
- acromion
- अधिवर्ध - epiphysis
- अवतलकार - concave
- उत्तलकार - convex
- उत्सेध - eminence
- उद्रेक - outburst
- उभार - condyle
- उलूखल - acetabulum
- कटक - ridge
- काण्ड - shaft
- काय - body
- किनारा - border
- कोण - angle
- खांच - notch,groove ,sulcus
- खुरदरी - rough
- गंडक - tuberosity
- गर्तिका - fovea
- गवाक्ष - fenestra
- गुलिका - tubercle
- गुहा - cavity
- घनाभ - cuboidal
- चक्रिकाएँ - disc
- चाप - arch
- छोर - end , pole
- द्वार - opening
- पृष्ठ , फलक - facet
- प्रशाखा - ramus
- रन्द्र - foramen
- वक्र - curve
- विदर - fissure
- विभंग - opening
- विवर - sinus
- शिखा - crest
- सतह - surface
- सिर - head
- सीवन - suture
- सौंफ - fennel
- part - pars
- margin - margo
- crest , ridge - crista
- line - linea
- notch - incisura
- groove - sulcus
- arch - arcus
- fontanelle - fonticuli
- fissure - fissura
- table - lamina
- roof - paries superior
- floor - paries inferior
- anterior - anterius
- posterior - posterius
- middle - medius
- surface - facies
- border - margo
- angle - angulus
- plane - planum
- corpus - body
- wing - ala
- lesser - minor , minus
- greater - major , majus
- plate - lamina
- ring - annulus
- horn - cornu
- true - verae
- floating - fluctuantes
- false - spurious
- supraglabellaris f. — अधिभ्रूकटक खात
- cerebella f. — अनुमस्तिष्क खात
- cubital f. — कफोणि खात, क्यूबिटल खात
- inguinal f. — वंक्षण खात
- ischiorectal f. — आसनास्थिमलाशय खात
- ovarian f. — डिंब ग्रंथि खात
- pararectal f. — परामलाशय खात
- paravesical f. — परावस्ति खात
- piriform f. — तुंबी खात
- popliteal f. — जानुपृष्ठ खात
- supravesical f. — अधि वस्ति खात
- sylvian f. — सिल्वियन खात
- triangular f. — त्रिकोण खात
- urethrae f. (fossa terminalis of male utethra) — (पुंमूत्रमार्ग का अंत्य खात)
- f. ovalis — अंडाकार खात
- f. terminalis — अंत्य खात


































Discussion