This is an old revision of the document!
SCALP
- Roof of head
- SCALP
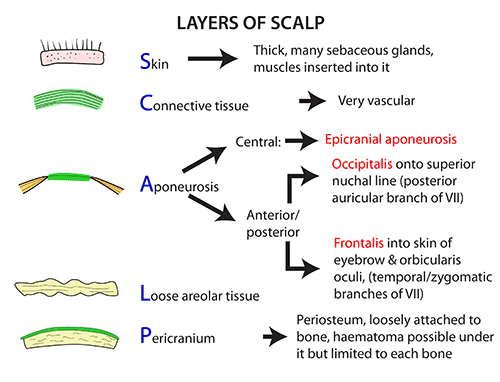
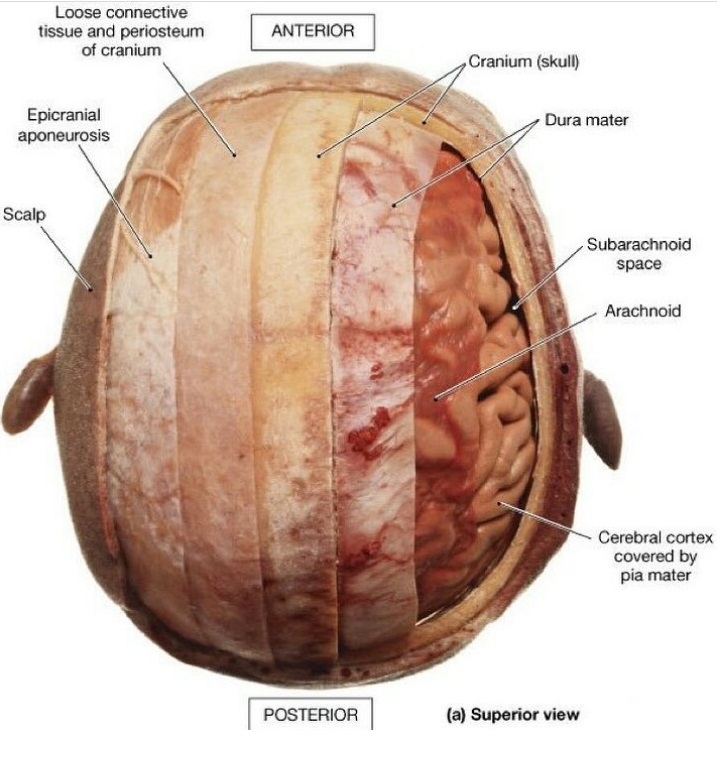
- S - contains numerous hair follicles and sebaceous glands (thus a common site for sebaceous cysts).
- C - dense connective tissue
- connects the skin to the epicranial aponeurosis.
- It is richly vascularised and innervated.
- The blood vessels within the layer are highly adherent to the connective tissue.
- This renders them unable to constrict fully if lacerated –
- and so the scalp can be a site of profuse bleeding.
- A - Epicranial Aponeurosis
- a thin, tendon-like structure that connects the occipitalis and frontalis muscles.
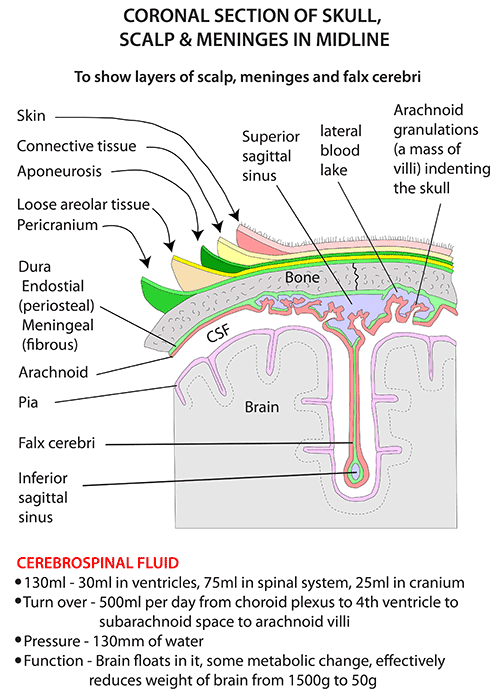
- L - loose areolar connective tissue
- a thin connective tissue layer that separates the periosteum of the skull
- from the epicranial aponeurosis.
- It contains numerous blood vessels, including emissary veins
- which connect the veins of the scalp to the diploic veins and intracranial venous sinuses.
- P - Periosteium
- the outer layer of the skull bones.
- It becomes continuous with the endosteum at the suture lines.
- Nerve supply
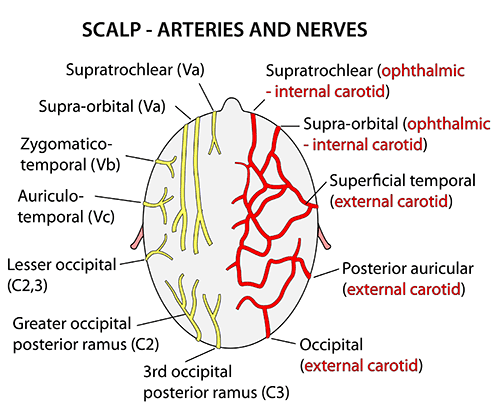
- Blood supply
- external carotid artery
- Superficial temporal – supplies the frontal and temporal regions
- Posterior auricular – supplies the area superiorly and posteriorly to the auricle.
- Occipital – supplies the back of the scalp
- Internal carotid artery
- ophthalmic artery
- the supraorbital
- supratrochlear arteries.
- Venous drainage
- The superficial drainage follows the arterial supply: superficial temporal, occipital, posterior auricular, supraorbital and supratrochlear veins.
- The deep (temporal) region of the skull is drained by the pterygoid venous plexus.
- Lymphatic drainage
Discussion