CEREBRUM
- CEREBRUM
- Divided in to two halves by a longitudinal cerebral fissure
- Features of longitudinal cerebral fissure
- cleft is complete
- except for the central part where it is joined by corpus callosum
- cleft is occupied by
- falx cerebri ( sickle shaped fold of duramater)
- fold of arachnoid that follows surfaces of falx cerebri
- piamater covering medial surface of falx cerebri
- anterior cerebral arteries and veins
- Each Cerebral hemisphere
- outer zone
- outer layer of grey matter called cerebral cortex
- inner zone
- inner mass of white matter
- large masses of subcortical grey matter
- EXTERNAL FEATURES
- POLES OR ENDS
- anterior end of the hemisphere
- frontal pole
- posterior end of hemisphere
- occipital pole
- below and in front
- temporal pole
- SURFACES
- BORDERS
- Superomedial border
- superciliary border
- Inferolateral border
- Medial orbital border
- Inferomedial or hippocampal border
- Medial occipital border
- SULCI AND GYRI
- Superolateral surface gyri and sulci
- frontal lobe
- precentral sulcus
- prefrontal sulcus
- superior and inferior frontal sulcus
- anterior and ascending rami of lateral sulcus
- divides the inferior frontal gyrus in to 3 parts
- part below anterior ramus is called pars orbitalis
- part between anterior and ascending rami is called pars triangularis
- part posterior to ascending ramus is called pars opercularis
- parietal lobe
- postcentral sulcus
- intraparietal sulcus
- temporal lobe
- superior , middle and inferior temporal gyrus
- superior and inferior temporal sulci
- Occipital lobe
- Lateral occipital sulcus
- lunate sulcus
- Transverse occipital sulcus
- Medial surface
- cingulate sulcus
- callosal sulcus
- Inferior surface
- Orbital part of inferior surface
- olfactory sulcus
- orbital sulcus
- Tentorial part of inferior surface
- Collateral sulcus
- Occipito-temporal sulcus
- LOBES
- Imaginary lines
- first imaginary line
- second imaginary line
- Frontal lobe
- anterior to central sulcus
- Parietal lobe
- behind central sulcus , in front of first imaginary line and above second imaginary line
- Temporal lobe
- below the posterior ramus of lateral sulcus and second imaginary line
- Occipital lobe
- parietooccipital sulcus and lower part of first imaginary line
- Insula / Island of reil ( Central Lobe )
- submerged or hidden portion of cerebral cortex in floor of lateral sulcus
- triangular in shape
- surrounded on all sides by a sulcus
- circular sulcus
- except anteroinferiorly at its apex
- limen insulae
- continuous with anterior perforate substance
- divided in to two regions by a central sulcus
- anterior region presents
- 3 or 4 gyri brevia
- posterior region presents
- 1 or 2 long gyri called gyri longa
- insula is hidden from surface view
- areas are called as opercula
- frontal , frontoparietal , temporal opercula
- CORTEX
- Types
- Allocortex
- archicortex
- paleocortex
- Neocortex
- 90% of the total area of cerebral cortex
- consists of 6 layers
- Variations in cortical structure
- Homotypical cortex
- Heterotypical cortex
- granular cortex
- granular layers are well developed
- pyramidal layers are poorly developed
- characteristic feature of sensory areas
- primary sensory , primary acoustic and visual areas
- Agranular cortex
- granular layers are poorly developed
- pyramidal layers are well developed
- characteristic feature of motor areas
- primary motor and other areas of frontal lobe
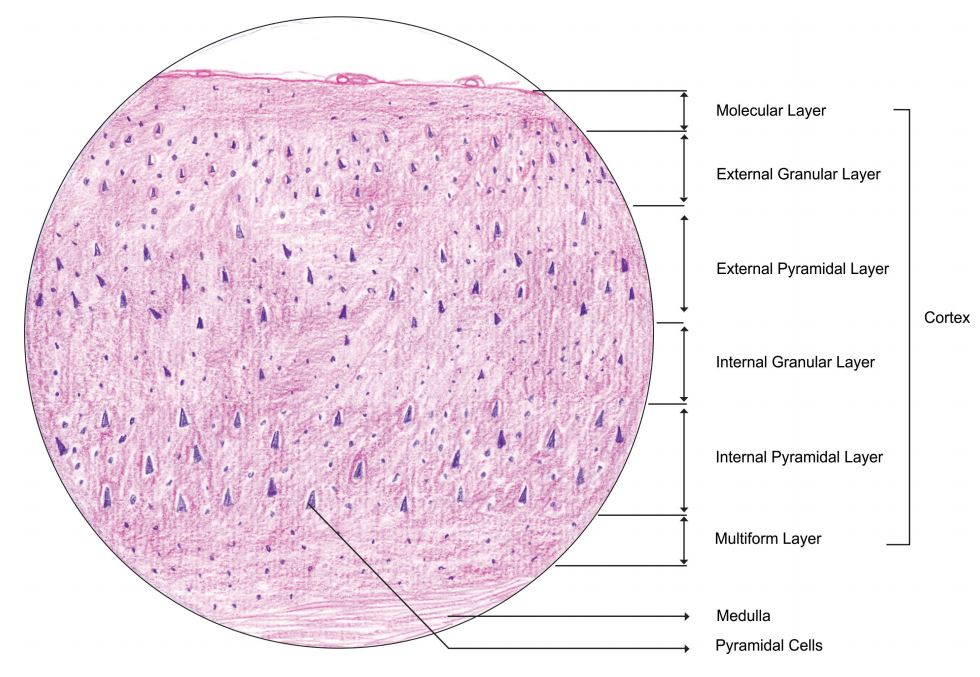
- histological layers of cerebral cortex
- molecular or plexiform layer
- external granular layer
- external pyramidal layer
- internal granular layer
- internal pyramidal ( ganglionic ) layer
- multiform layer ( layer of polymorphic cells )
- histologically types of neurons
- pyramidal cells
- stellate or granule cells
- fusiform cells
- horizontal cells of cajal
- cells of martinotti
- connecting neurons are by three ways
- projection neurons
- association neurons
- commissural neurons
- Functional areas of cerebral cortex
- Types of cortical areas
- sensory area
- motor area
- association area
The vertebrate cerebrum (brain) is formed by two cerebral hemispheres that are separated by a groove, the longitudinal fissure. The brain can thus be described as being divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres. Each of these hemispheres has an outer layer of grey matter, the cerebral cortex, that is supported by an inner layer of white matter. In eutherian (placental) mammals, the hemispheres are linked by the corpus callosum, a very large bundle of nerve fibers. Smaller commissures, including the anterior commissure, the posterior commissure and the fornix, also join the hemispheres and these are also present in other vertebrates. These commissures transfer information between the two hemispheres to coordinate localized functions.
There are three known poles of the cerebral hemispheres: the occipital pole, the frontal pole, and the temporal pole.
| LATIN OR ENGLISH | SIMPLE ENGLISH |
|---|---|
| cerebrum | Brainwall |
| frontal lobe | Frontbrainwall |
| parietal lobe | BrainRoof |
| temporal lobe | Brainsidewall |
| occipital lobe | Backbrainwall |
| limbic lobe | Brainmedialwalls |
The central sulcus is a prominent fissure which separates the parietal lobe from the frontal lobe and the primary motor cortex from the primary somatosensory cortex.
FEATURES
CEREBRAL HEMISPHERE
SUPEROLATERAL SURFACE
- The central sulcus is a sulcus, or groove, in the cerebral cortex in the brains of vertebrates. Also called the central fissure, or the fissure of Rolando or the Rolandic fissure, after Luigi Rolando. It is sometimes confused with the longitudinal fissure.The central sulcus is a prominent landmark of the brain, separating the parietal lobe from the frontal lobe and the primary motor cortex from the primary somatosensory cortex.
- The lateral sulcus (also called Sylvian fissure or lateral fissure) is one of the most prominent features of the human brain. The lateral sulcus is a deep fissure in each hemisphere that separates the frontal and parietal lobes from the temporal lobe. The insular cortex lies deep within the lateral sulcus.The lateral sulcus has a number of side branches. Two of the most prominent and most regularly found are the ascending (also called vertical) ramus and the horizontal ramus of the lateral fissure, which subdivide the inferior frontal gyrus. The lateral sulcus also contains the transverse temporal gyri, which are part of the primary and below the surface auditory cortex.
- The precentral sulcus is a part of the human brain that lies parallel to, and in front of, the central sulcus. (A sulcus is one of the prominent grooves on the surface of the human brain.The precentral sulcus divides the inferior, middle and superior frontal gyri from the precentral gyrus. In most brains, the precentral sulcus is divided into two parts: the inferior precentral sulcus and the superior precentral sulcus. However, the precentral sulcus may sometimes be divided into three parts or form one continuous sulcus.
- The inferior surface of the temporal lobe is concave, and is continuous posteriorly with the tentorial surface of the occipital lobe. It is traversed by the inferior temporal sulcus, which extends from near the occipital pole behind, to within a short distance of the temporal pole in front, but is frequently subdivided by bridging gyri.
- The superior temporal sulcus (STS) is the sulcus separating the superior temporal gyrus from the middle temporal gyrus in the temporal lobe of the brain. A sulcus (plural sulci) is a deep groove that curves into the largest part of the brain, the cerebrum, and a gyrus (plural gyri) is the a ridge that curves outward of the cerebrum.
- In brain anatomy, the lunate sulcus or simian sulcus also known as the sulcus lunatus is a fissure in the occipital lobe variably found in humans and more often larger when present in apes and monkeys.The lunate sulcus marks the transition between V1 and V2.
MEDIAL SURFACE
- SULCI
- Anterior paraolfactory
- posterior paraolfactory
- cingulate
- callosal
- suprasplenial or subparietal
- parieto-occipital
- calcarine
- GYRI
- paraolfactory
- Paraterminal
- medial frontal
- paracentral lobule
- cingulate
- cuneus
- precuneus
BORDERS
- superomedial border
- inferolateral border
- medial orbital border
- medial occipital border
POLES
- frontal pole
- occipital pole
- temporal pole
LOBES
FUNCTIONAL AREAS OF CEREBRAL CORTEX
SENSORY AREA
MOTOR AREA
GYRUS AND SULCUS OF BRAIN
GYRI AND SULCUS OF BRAIN FUNCTIONS
| 973 | TELENCEPHALON; CEREBRUM | TELENCEPHALON; CEREBRUM | ||
| 974 | Hemispherium cerebri | Cerebral hemisphere | ||
| 975 | Pallium | Cerebral cortex | ||
| 976 | Gyri cerebri | Cerebral gyri | ||
| 977 | Lobi cerebri | Cerebral lobes | ||
| 978 | Sulci cerebri | Cerebral sulci | ||
| 979 | Fissura longitudinalis cerebri | Longitudinal cerebral fissure | ||
| 980 | Fissura transversa cerebri | Transverse cerebral fissure | ||
| 981 | Fossa lateralis cerebri | Lateral cerebral fossa | ||
| 982 | Margo superior | Superior margin | ||
| 983 | Margo inferomedialis | Inferomedial margin | ||
| 984 | Margo inferolateralis | Inferolateral margin | ||
| 985 | Facies superolateralis hemispherii cerebri | Superolateral face of cerebral hemisphere | ||
| 986 | Sulci interlobares | Interlobar sulci | ||
| 987 | Sulcus centralis | Central sulcus | ||
| 988 | Sulcus lateralis Sylvii | Lateral sulcus Sylvii | ||
| 989 | Ramus posterior | Posterior ramus | ||
| 990 | Ramus ascendens | Ascending ramus | ||
| 991 | Ramus anterior | Anterior ramus | ||
| 992 | Sulcus parietooccipitalis | Parieto-occipital sulcus | ||
| 993 | Incisura preoccipitalis | Preoccipital notch | ||
| 994 | Lobus frontalis | Frontal lobe | ||
| 995 | Polus frontalis | Frontal pole | ||
| 996 | Operculum frontale | Frontal operculum | ||
| 997 | Gyrus frontalis inferior | Inferior frontal gyrus | ||
| 998 | Pars orbitalis | Orbital part | ||
| 999 | Pars triangularis | Triangular part | ||
| 1000 | Pars opercularis | Opercular part | ||
| 1001 | Sulcus frontalis inferior | Inferior frontal sulcus | ||
| 1002 | Gyrus frontalis medius | Middle frontal gyrus | ||
| 1003 | Gyrus precentralis | Precentral gyrus | ||
| 1004 | Sulcus precentralis | Precentral sulcus | ||
| 1005 | Gyrus frontalis superior | Superior frontal gyrus | ||
| 1006 | Sulcus frontalis superior | Superior frontal sulcus | ||
| 1007 | Lobus parietalis | Parietal lobe | ||
| 1008 | Gyrus angularis | Angular gyrus | ||
| 1009 | Lobulus parietalis inferior | Inferior parietal lobule | ||
| 1010 | Operculum parietale | Parietal operculum | ||
| 1011 | Sulcus intraparietalis | Intraperietal sulcus | ||
| 1012 | Gyrus postcentralis | Postcentral gyrus | ||
| 1013 | Sulcus postcentralis | Postcentral sulcus | ||
| 1014 | Lobulus parietalis superior | Superior parietal lobule | ||
| 1015 | Gyrus supramarginalis | Supramarginal gyrus | ||
| 1016 | Lobus occipitalis | Occipital lobe | ||
| 1017 | Polus occipitalis | Occipital pole | ||
| 1018 | Sulcus lunatus | Lunate sulcus | ||
| 1019 | Incisura preoccipitalis | Preoccipital notch | ||
| 1020 | Sulcus occipitalis transversus | Transverse occipital sulcus | ||
| 1021 | Lobus temporalis | Temporal lobe | ||
| 1022 | Polus temporalis | Temporal pole | ||
| 1023 | Gyrus temporalis superior | Superior temporal gyrus | ||
| 1024 | Operculum temporale | Temporal operculum | ||
| 1025 | Gyri temporales transversi Heschl | Transverse temporal gyri Heschl's gyri | ||
| 1026 | Gyrus temporalis transversus anterior | Anterior transverse temporal gyrus | ||
| 1027 | Gyrus temporalis transversus posterior | Posterior transverse temporal gyrus | ||
| 1028 | Planum temporale | Temporal plane | ||
| 1029 | Sulcus temporalis transversus | Transverse temporal sulcus | ||
| 1030 | Sulcus temporalis superior | Superior temporal sulcus | ||
| 1031 | Gyrus temporalis medius | Middle temporal gyrus | ||
| 1032 | Sulcus temporalis inferior | Inferior temporal sulcus | ||
| 1033 | Gyrus temporalis inferior | Inferior temporal gyrus | ||
| 1034 | Insula; lobus insularis | Insula; insular lobe | ||
| 1035 | Gyri insulae | Insular gyri | ||
| 1036 | Gyrus longus insulae | Long gyrus of insula | ||
| 1037 | Gyri breves insulae | Short gyri of insula | ||
| 1038 | Sulcus centralis insulae | Central sulcus of insula | ||
| 1039 | Sulcus circularis insulae | Circular sulcus of insula | ||
| 1040 | Limen insulae | Limen insulae; insular threshold | ||
| 1041 | Facies inferomedialis hemispherii cerebri | Medial and inferior surfaces of cerebral hemisphere | ||
| 1042 | Sulci interlobares | Interlobar sulci | ||
| 1043 | Sulcus corporis callosi | Sulcus of corpus callosum | ||
| 1044 | Sulcus cinguli | Cingulate sulcus | ||
| 1045 | Ramus marginalis; sulcus marginalis | Marginal branch; marginal sulcus | ||
| 1046 | Sulcus subparietalis | Subparietal sulcus | ||
| 1047 | Sulcus parietooccipitalis | Parieto-occipital sulcus | ||
| 1048 | Sulcus collateralis | Collateral sulcus | ||
| 1049 | Sulcus centralis | Central sulcus | ||
| 1050 | Lobus frontalis | Frontal lobe | ||
| 1051 | Gyrus frontalis medialis | Medial frontal gyrus | ||
| 1052 | Sulcus paracentralis | Paracentral sulcus | ||
| 1053 | Lobulus paracentralis | Paracentral lobule | ||
| 1054 | Gyrus paracentralis anterior | Anterior paracentral gyrus | ||
| 1055 | Sulcus centralis | Central sulcus | ||
| 1056 | Area subcallosa | Subcallosal area; subcallosal gyrus | ||
| 1057 | Gyrus paraterminalis | Paraterminal gyrus | ||
| 1058 | Area paraolfactoria | Paraolfactory area | ||
| 1059 | Gyri paraolfactorii | Paraolfactory gyri | ||
| 1060 | Sulci paraolfactorii | Paraolfactory sulci | ||
| 1061 | Gyri orbitales | Orbital gyri | ||
| 1062 | Sulci orbitales | Orbital sulci | ||
| 1063 | Gyrus rectus | Straight gyrus | ||
| 1064 | Sulcus olfactorius | Olfactory sulcus | ||
| 1065 | Gyrus olfactorius lateralis | Lateral olfactory gyrus | ||
| 1066 | Gyrus olfactorius medialis | Medial olfactory gyrus | ||
| 1067 | Lobus parietalis | Parietal lobe | ||
| 1068 | Lobulus paracentralis | Paracentral lobule | ||
| 1069 | Gyrus paracentralis posterior | Posterior paracentral gyrus | ||
| 1070 | Precuneus | Precuneus | ||
| 1071 | Sulcus subparietalis | Subparietal sulcus | ||
| 1072 | Sulcus parietooccipitalis | Parieto-occipital sulcus | ||
| 1073 | Ramus marginalis; sulcus marginalis | Marginal branch; marginal sulcus | ||
| 1074 | Lobus occipitalis | Occipital lobe | ||
| 1075 | Cuneus | Cuneus | ||
| 1076 | Sulcus calcarinus | Calcarine sulcus | ||
| 1077 | Gyrus lingualis | Lingual gyrus | ||
| 1078 | Gyrus occipitotemporalis lateralis | Lateral occipitotemporal gyrus | ||
| 1079 | Gyrus occipitotemporalis medialis | Medial occipitotemporal gyrus | ||
| 1080 | Sulcus occipitotemporalis | Occipitotemporal sulcus | ||
| 1081 | Sulcus parietooccipitalis | Parieto-occipital sulcus | ||
| 1082 | Lobus temporalis | Temporal lobe | ||
| 1083 | Sulcus collateralis | Collateral sulcus | ||
| 1084 | Gyrus occipitotemporalis medialis | Medial occipitotemporal gyrus | ||
| 1085 | Sulcus occipitotemporalis | Occipitotemporal sulcus | ||
| 1086 | Gyrus occipitotemporalis lateralis | Lateral occipitotemporal gyrus | ||
| 1087 | Sulcus temporalis inferior | Inferior temporal sulcus | ||
| 1088 | Gyrus temporalis inferior | Inferior temporal gyrus | ||
| 1089 | Lobus limbicus | Limbic lobe | ||
| 1090 | Sulcus cinguli | Cingulate sulcus | ||
| 1091 | Gyrus cinguli | Cingulate gyrus | ||
| 1092 | Isthmus gyri cinguli | Isthmus of cingulate gyrus | ||
| 1093 | Gyrus fasciolaris | Fasciolar gyrus | ||
| 1094 | Gyrus parahippocampalis | Parahippocampal gyrus | ||
| 1095 | Uncus | Uncus | ||
| 1096 | Sulcus hippocampalis | Hippocampal sulcus | ||
| 1097 | Gyrus dentatus | Dentate gyrus | ||
| 1098 | Sulcus fimbriodentatus | Fimbriodentate sulcus | ||
| 1099 | Fimbria hippocampi | Fimbria of hippocampus | ||
| 1100 | Sulcus collateralis | Collateral sulcus | ||
| 1101 | Sulcus rhinalis | Rhinal sulcus |
| 1155 | Cortex cerebri | Cerebral cortex | ||
| 1156 | Archicortex | Archicortex | ||
| 1157 | Paleocortex | Paleocortex | ||
| 1158 | Neocortex | Neocortex | ||
| 1159 | Allocortex | Allocortex | ||
| 1160 | Mesocortex | Mesocortex | ||
| 1161 | Isocortex | Isocortex | ||
| 1162 | Strata isocorticis | Layers of isocortex | ||
| 1163 | Lamina molecularis [lamina I] | Molecular layer [layer I] | ||
| 1164 | Lamina granularis externa [lamina II] | External granular layer [layer II] | ||
| 1165 | Lamina pyramidalis externa [lamina III] | External pyramidal layer [layer III] | ||
| 1166 | Lamina granularis interna [lamina IV] | Internal granular layer [layer IV] | ||
| 1167 | Lamina pyramidalis interna [lamina V] | Internal pyramidal layer [layer V] | ||
| 1168 | Lamina multiformis [lamina VI] | Multiform layer [layer VI] | ||
| 1169 | Stria laminae molecularis | Stria of molecular layer | ||
| 1170 | Stria laminae granularis externae | Stria of external granular layer | ||
| 1171 | Stria laminae granularis internae | Stria of internal granular layer | ||
| 1172 | Stria occipitalis Gennari | Occipital stripe; occipital line Gennari | ||
| 1173 | Stria laminae pyramidalis internae | Stria of internal pyramidal layer | ||
| 1174 | Neurofibrae tangentiales | Tangential fibres |
Discussion