Classification
Motions are classified after the anatomical planes they occur in, although movement is more often than not a combination of different motions occurring simultaneously in several planes. Motions can be split into categories relating to the nature of the joints involved:
- Gliding motions(फिसलन गतिविधि ) इसलिए होती हैं क्यूंकी सापेक्षिक सपाट हड्डी कि सतह एक दूसरे के ऊपर गति करती हैं , लेकिन वे हड्डियों कि बहुत कम गति पैदा करती हैं |
- Angular motions(कोणीय गतिविधि ) occur over synovial joints and causes them to either increase or decrease angles between bones.
- Rotational motions (घूर्णन गतिविधि ) में इसके अनुदैर्ध्य अक्ष के चारों ओर हड्डियों का घुमाना शामिल होता हैं , यह शरीर के मध्य रेखा कि ओर (माध्यम घूर्णी ) , या शरीर के मध्य रेखा से दूर (पार्श्व घूर्णी ) कर सकता हैं | गतिविधि जैसे सिर को दूसरी तरफ देखने के लिए सिर घुमाना
Apart from this motions can also be divided into:
Linear motions (or translatory motions), which move in a line between two points. Rectilinear motion is motion in a straight line between two points, whereas curvilinear motion is motion following a curved path. Angular motions (or rotary motions) occur when an object is around another object increasing or decreasing the angle. The different parts of the object do not move the same distance. Examples include a movement of the knee, where the lower leg changes angle compared to the femur, or movements of the ankle. The study of movement is known as kinesiology. A categoric list of movements of the human body and the muscles involved can be found at list of movements of the human body.
Abnormal motion The prefix hyper- is sometimes added to describe movement beyond the normal limits, such as in hypermobility, hyperflexion or hyperextension. The range of motion describes the total range of motion that a joint is able to do. For example, if a part of the body such as a joint is overstretched or bent backwards because of exaggerated extension motion, then it can be described as hyperextended. Hyperextension increases the stress on the ligaments of a joint, and is not always because of a voluntary movement. It may be a result of accidents, falls, or other causes of trauma. It may also be used in surgery, such as in temporarily dislocating joints for surgical procedures. Or it may be used as a pain compliance method to force a person to take a certain action, such as allowing a police officer to take him into custody.
| Extension | प्रसार | Extensor | प्रसारिणी | सामान्य अंगुलिप्रसारिणी (extensor digitorum communis) | |
| Flexion | आंकुचन | Flexor | आकुंचनी | ||
| Extension | विस्तार | Extensor | |||
| Adduction | अभिवर्तन / अभिसंयोगः | Adductor | अभिवर्तनी | ||
| Abduction | अपवर्तन / विसंयोगः | Abductor | अपवर्तनी | कनिष्ठा अपर्वतनी (abductor digiti quinti), | |
| Rotation | घूर्णन | Rotator | eye rotation , lateral rotation , medial rotation | ||
| Circumduction | पर्यावर्तन | ||||
| Supination | उत्तानन / वक्षोभि: प्रक्षेपणम् | Supinator | उत्ताननी | ||
| Pronation | अवतानन / वक्षोभि: प्रवर्तनम् | Pronator | अवतानिका | वर्तु अवताननी (pronator teris), | |
| Depression | अवनमन / अवतोलनम् | Depressor | अवनमनी | wrinkle eyebrows , close eyelid | नासापट अवनमनी (depressor septi) |
| Elevation | उत्थानन / उन्नमन / उत्कर्षण / उत्तोलनम् | Levator | उन्नमनी | raise eyebrows , open eyelid , elevate upper lip , elevate nose septum | अधर उन्नमनी (mentalis) , भ्रूनमनी (procerus) |
| Opposition | व्यावर्तन | Opponens | व्यावर्तिका | ||
| Compression | संपीड़न | Compressor | संपीडनी | compress nostril | कपोल संपीडनी (buccinator) , परापिंडिका (gastrocnemius),पिंडिका (soleus), |
| Retraction | अपकर्षण / अन्तर्धान / अभिच्छायन / प्रतिच्छायन | Retractor | retract scalp , | ||
| Inversion | विपरिवर्तन / प्रदक्षिण | Inverter | अंर्तवर्तक | ||
| Eversion | बहीवर्तन / पूर्वोत्तर | Everter | उद्वर्ती | ||
| Protrusion | प्रलंबन / उद्गमन / प्रोच्छायन | Protruder | |||
| Protraction | विलंबन | Protractor | |||
| chewing | चर्वण | चर्वणी (masseter), | |||
| Intorsion | आन्तरवर्तनम् | ||||
| Extorsion | बहिर्वर्तनम् | ||||
| contraction | |||||
| relaxation | |||||
| systole | सिकुड़न / प्रकुंचन | ||||
| diastole | शिथिलन | ||||
| peristalsis | क्रमांकुचन | ||||
| Tension | तानन | tensor | तानिका | ||
| opening | विकासन | ||||
| closing | संकुचन |
General motion
These are general terms that can be used to describe most movements the body makes. Most terms have a clear opposite, and so are treated in pairs.
आंकुचन और विस्तार
आंकुचन(FLEXION) और विस्तार (EXTENSION) Flexion and extension describe movements that affect the angle between two parts of the body. These terms come from the Latin words with the same meaning. आंकुचन describes a bending movement that decreases the angle between a segment and its proximal segment. For example, bending the elbow, or clenching a hand into a fist, are examples of flexion. When a person is sitting down, the knees are flexed. When a joint can move forward and backward, such as the neck and trunk, flexion is movement in the anterior direction.When the chin is against the chest, the head is flexed, and the trunk is flexed when a person leans forward. Flexion of the shoulder or hip is movement of the arm or leg forward.
विस्तार या प्रसार is the opposite of flexion, describing a straightening movement that increases the angle between body parts. For example, when standing up, the knees are extended. When a joint can move forward and backward, such as the neck and trunk, extension is movement in the posterior direction.[10] Extension of the hip or shoulder moves the arm or leg backward. Hyperextension is any extension that goes beyond 180 degrees and becomes reflexive.
With regard to the toes, flexion means curling them downward whereas extension means uncurling them or raising them upward.
| radial deviation |  | Radial deviation is the hand moving towards the radial styloid (or, towards the thumb/first digit). Abduction of the wrist is also called radial deviation |
| ulnar deviation |  | Ulnar deviation is the hand moving towards the ulnar styloid (or, towards the pinky/fifth digit). |
| अंगुली का अंकुचन या मोड़ना |  | |
| अंगुली का अपवर्तन |  | In the case of fingers and toes, it is spreading the digits apart, away from the centerline of the hand or foot |
| अंगुली का अभिवर्तन |  | it is bringing the digits together, towards the centerline of the hand or foot |
| अंगुली का विस्तार |  | |
| अंगूठे का अपवर्तन | 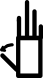 | |
| अंगूठे का अभिवर्तन |  | |
| अंगूठे का मोड़ना |  | |
| अंगूठे का विस्तार | 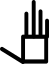 | |
| अंदरूनी घूर्णन | Internal rotation (medial rotation or intorsion) is rotation towards the axis of the body. | |
| अंसफलक का अवनमन या गिराना | Depression is movement in an inferior direction, | |
| अंसफलक का उन्नमन या उठान | Elevation is movement in a superior direction.For example, shrugging is an example of elevation of the scapula. | |
| कंधे का अपवर्तन |  | |
| कंधे का अभिवर्तन | 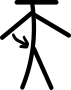 | |
| कंधे का पर्यावर्तन |  | |
| कंधे का मोड़ना |  | |
| कंधे का विस्तार | 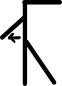 | |
| कलाई का मोड़ना या अंकुचन | 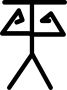 | |
| कलाई का विस्तार |  | |
| कोहनी का प्रसार |  | |
| कोहनी को मोड़ना या संकुचन |  | |
| गर्दन का मोड़ना या अंकुचन | 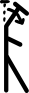 | |
| गर्दन का विस्तार | 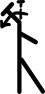 | |
| घुटने का अंकुचन या मोड़ना |  | |
| घुटने का विस्तार | 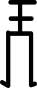 | |
| तलवे का मोड़ना का अंकुचन |  | Plantar flexion or plantarflexion is the movement which decreases the angle between the sole of the foot and the back of the leg; for example, the movement when depressing a car pedal or standing on tiptoes |
| धड़ का मोड़ना या अंकुचन |  | |
| धड़ का विस्तार |  | |
| नितंब अपवर्तन |  | |
| नितंब अभिवर्तन |  | |
| नितंब का अंदरूनी घूर्णन |  | |
| नितंब का पार्श्व घूर्णन |  | |
| नितंब का बाहरी घूर्णन |  | |
| नितंब का मध्य घूर्णन | 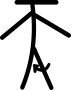 | |
| पादुका का बहीवर्तन |  | Eversion is the movement of the sole of the foot away from the median plane |
| पादुका का विपरिवर्तन |  | Inversion is the movement of the sole towards the median plane. For example, inversion describes the motion when an ankle is twisted. |
| पादुका या पैर को मोड़ना |  | Dorsiflexion is where the toes are brought closer to the shin. This decreases the angle between the dorsum of the foot and the leg. For example, when walking on the heels the ankle is described as being in dorsiflexion |
| बाहरी घूर्णन | External rotation (lateral rotation or extorsion) is rotation away from the center of the body. | |
| भुज का अंदरूनी घूर्णन | 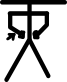 | |
| भुजा का बाहरी घूर्णन |  | |
| हथेली का मोड़ना या अंकुचन |  | Palmarflexion is flexion of the wrist towards the palm and ventral side of forearm. |
| हथेली को पीछे कि तरफ मोड़ना |  | Dorsiflexion is hyperextension of the wrist joint, towards the dorsal side of forearm. |
| हाथ का अवतानन |  | prone (facing down) , Pronation at the forearm is a rotational movement where the hand and upper arm are turned so the thumbs point towards the body |
| हाथ का उत्तानन |  | supine (facing up) , When the forearm and hand are supinated, the thumbs point away from the body. |

Discussion