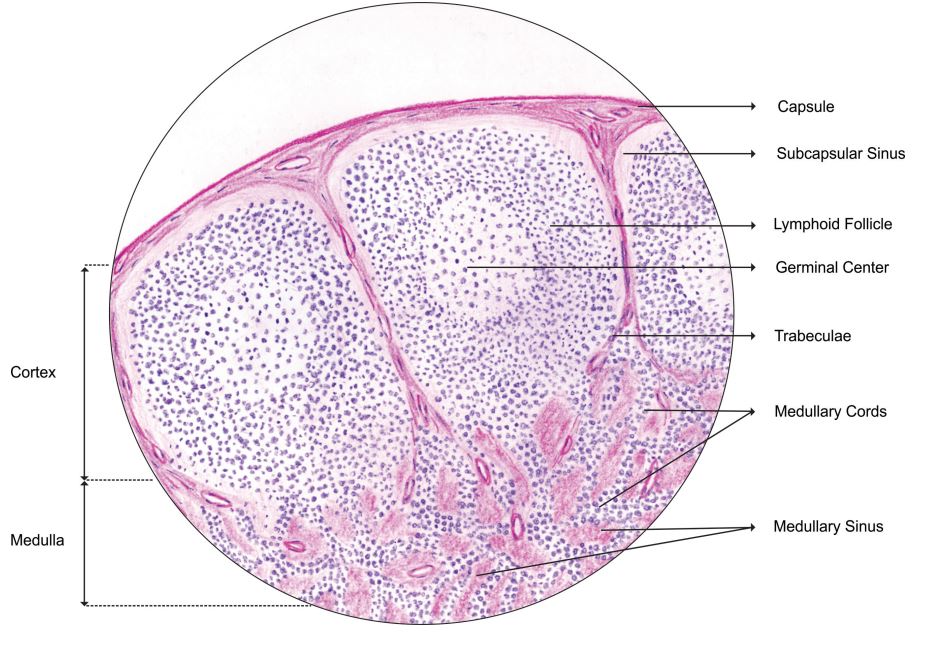
LYMPH NODE
- Afferent lymph vessels:
- Penetrate capsule, enter marginal sinus, communicate with intranodal sinuses, then become efferent vessels, which lack an endothelial lining
- Intranodal vessels contain littoral cells or histiocytes with phagocytic properties
- Capsule:
- Cortex:
- Subcapsular portion of node with largest number of follicles (primary or secondary)
- Primary follicle:
- Round aggregates of small, dark staining inactive (naïve) B lymphocytes, usually near the capsule, within a network of follicular dendritic cell processes
- No germinal center present
- Secondary follicle:
- Arises from primary follicle that develops germinal centers (see below) due to antigenic stimulation of B cells and production of antibodies
- Contains pale staining germinal center which may be polarized towards site of antigen entry
- Surrounded by mantle zone and marginal zone lymphocytes
- Germinal center:
- Contains predominantly B lymphocytes (including centroblasts and centrocytes) and scattered follicular T helper cells and T regs
- Also tingible body macrophages and follicular dendritic cells
- Mantle zone:
- Tightly packed small B lymphocytes of the primary follicles, pushed aside by the germinal centers
- Marginal zone:
- Paracortex:
- Tissue between cortical follicles and medulla (see below)
- Contains predominantly dark staining mature T cells, B immunoblasts, interdigitating dendritic cells, plasmacytoid dendritic cells, histiocytes and high endothelial venules (postcapillary venules lined by plump endothelial cells that express leukocyte adhesion molecules and contain intraluminal lymphocytes)
- Expands during cell mediated immunological reactions
- Has coarse network of reticulin fibers
- Medulla:
- Portion of node closest to hilum
- Contains the medullary cords, sinuses and vessels but minimal number of follicles
- Medullary cords:
- Found in hilar region between the sinuses, composed mostly of small B and T lymphocytes, plasmacytoid lymphocytes, plasmablasts and plasma cells
- Sinuses:
- Carry lymph from afferent to efferent lymphatics
- Subcapsular sinus is below capsule and partially lined by endothelium
- Becomes medullary as it approaches the hilum and is lined by macrophages
- Also contains mast cells and plasma cells
- Vessels:
- Blood enters and leaves lymph node at hilus
Discussion